student | Posted on
BF3 is a covalent compound as it is formed by sharing of electrons. Its name is Boron Trifluoride. It is sp2 hybridized. As far as its polarity is concerned, BF3 is a non-polar molecule. The electronegative fluorine atoms are in the triangular planar structure. So, its net dipole moment results in zero. It has some dipole moment but due to triangular structure, all the existing dipole moments will cancel out each other. That's why, BF3 is a non-polar molecule.
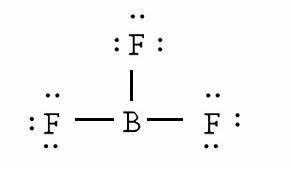
0
0 Comment
Fashion enthusiast | Posted on
BF3, also known as boron trifluoride, is a nonpolar molecule. This is because the molecule has a symmetrical trigonal planar shape and has no lone pairs of electrons on the central boron atom.
In a nonpolar molecule, the electronegativity difference between the atoms in the molecule is minimal, and the molecule has no permanent dipole moment. In the case of BF3, the three fluorine atoms are arranged symmetrically around the boron atom, with each fluorine atom pulling the shared electrons towards itself. This results in a balanced distribution of electron density around the central boron atom, which makes the molecule nonpolar.
The polarity of a molecule depends on various factors, including the shape of the molecule and the electronegativity difference between the atoms in the molecule. Electronegativity is the ability of an atom to attract electrons towards itself. In a polar molecule, there is a difference in electronegativity between the atoms, which results in an uneven distribution of electrons and the formation of a permanent dipole moment.
In contrast, in a nonpolar molecule, the electronegativity of the atoms is balanced, resulting in an even distribution of electrons and no permanent dipole moment. Therefore, BF3, which has a symmetrical trigonal planar shape and no lone pairs of electrons on the central boron atom, is a nonpolar molecule.
0
0 Comment
Student | Posted on
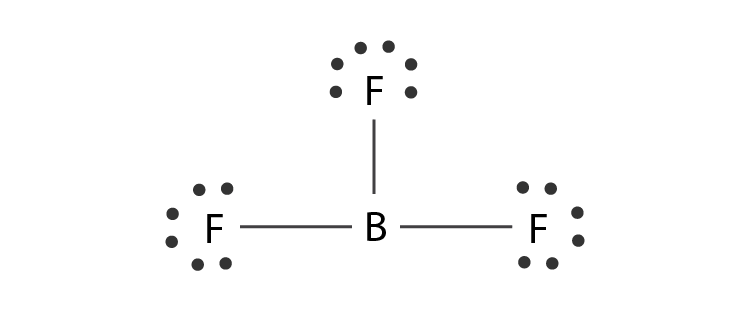
Polar: a molecule or ion that has at least one unpaired electron in its outermost orbital, therefore easily dissociating to form two covalent bonds.
0
0 Comment
| Posted on
Is BF3 Polar or Nonpolar?
In the world of chemistry, molecules are either polar or nonpolar. This polarity, or lack thereof, has a significant impact on the molecule's properties and behavior. Understanding whether a molecule is polar or nonpolar is essential for grasping fundamental chemical concepts and predicting molecular interactions.
In this blog post, we'll delve into the fascinating world of polarity and determine whether BF3, or boron trifluoride, is polar or nonpolar. We'll take a step-by-step approach, breaking down the concepts and providing clear explanations along the way.
Understanding Polarity
Before we dive into BF3 specifically, let's first establish a clear understanding of polarity. In simple terms, a polar molecule is one that has an uneven distribution of electrons. This uneven distribution creates a dipole moment, which is a measure of the separation of positive and negative charges within the molecule.
A nonpolar molecule, on the other hand, has a symmetrical distribution of electrons. This symmetry results in a zero dipole moment, meaning that the positive and negative charges cancel each other out.
Electronegativity and Bond Polarity
The polarity of a molecule is largely determined by the electronegativity of the atoms involved. Electronegativity is a measure of an atom's ability to attract electrons in a chemical bond. Atoms with higher electronegativity tend to attract electrons more strongly, creating a partial negative charge around them.
In a molecule with two different types of atoms, the atom with the higher electronegativity will attract electrons towards itself, leaving the other atom with a partial positive charge. This unequal distribution of electrons results in a polar bond.
Molecular Geometry and Net Dipole Moment
Even though individual bonds can be polar, a molecule may not necessarily be polar overall. The polarity of a molecule depends not only on the polarity of its bonds but also on its molecular geometry.
Molecular geometry is the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in a molecule. If the polar bonds in a molecule are arranged in a symmetrical way, the individual dipole moments will cancel each other out, resulting in a net dipole moment of zero. Such a molecule is considered nonpolar.
Determining the Polarity of BF3
Now, let's apply these concepts to BF3, or boron trifluoride. BF3 is a molecule with three fluorine atoms bonded to a central boron atom. The Lewis structure of BF3 shows that the fluorine atoms are arranged in a trigonal planar geometry, with bond angles of 120 degrees.
The bonds between boron and fluorine are polar, as fluorine has a higher electronegativity than boron. However, due to the trigonal planar geometry, the individual dipole moments of the B-F bonds are oriented in a way that cancels each other out. As a result, the net dipole moment of BF3 is zero, and the molecule is considered nonpolar.
Conclusion
Through a step-by-step approach, we've explored the concept of polarity and determined that BF3, or boron trifluoride, is a nonpolar molecule. We've learned that polarity arises from the uneven distribution of electrons and that molecular geometry plays a crucial role in determining whether a molecule is polar or nonpolar.
Understanding polarity is essential for comprehending various chemical phenomena, from intermolecular interactions to molecular reactivity. As you delve deeper into the world of chemistry, keep these concepts in mind to gain a clearer understanding of the intricate world of molecules and their properties.

0
0 Comment
